昨天我們在開發板上實驗,使用 MQTT 來收與發訊息,今天我們將這樣的機制整合到我們 DIY 的變頻風扇。
我想,最方便控制變頻風扇的方式,除了紅外線遙控器外,當屬幾乎不離手的手機了。其實設計一個具有 MQTT 收發功能的 app ,應該也不是太難!而且還有圖形化的開發環境 App inventor 可以用,但這些都超出我們今天要探討的範圍。而最簡單的方式,應該是找一個現成的 MQTT client 的 app 來使用。
我們以安卓手機爲例,在 google play 中查找 "MQTT dashboard" (MQTT 儀表板):
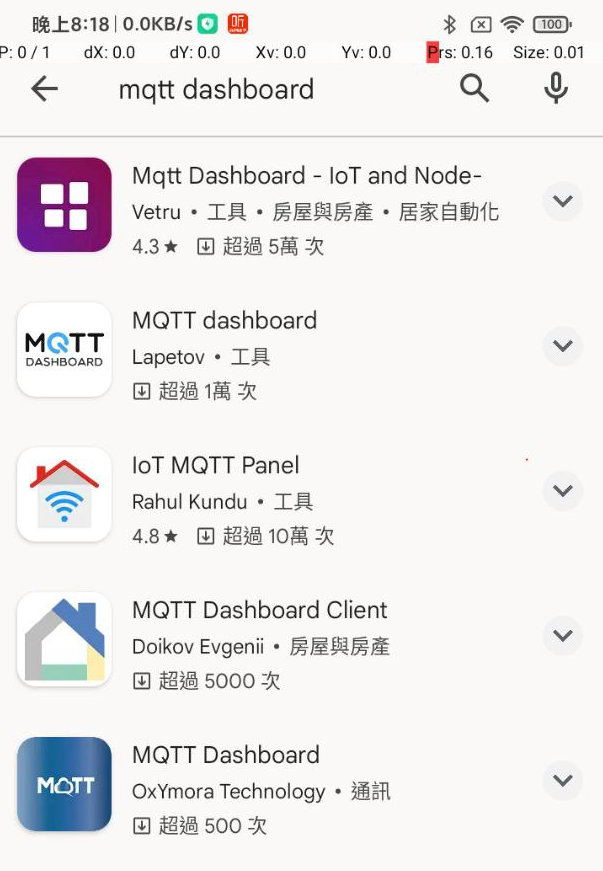
就選 google 挑的一個來安裝吧!
在這裡可以看到這個應用軟體完整的使用說明:https://vetru-apps.github.io/mqtt-dashboard-documentation/
執行 app 之後,我們可以按畫面最下面中間的 “+” 圖示,來增加一個 MQTT 伺服器(Broker):
Broker name: 最後顯示在軟體上面的名稱,可以是中文,注意:免費版本只能連上一個 Broker,可以加入其它的 Broker 服務器,但是必須升級爲 pro 版本才能啓用。
Address: 就填入我們測試用的 MQTT broker 地址, “test.mosquitto.org" 即可
其它欄位就使用默認值即可。
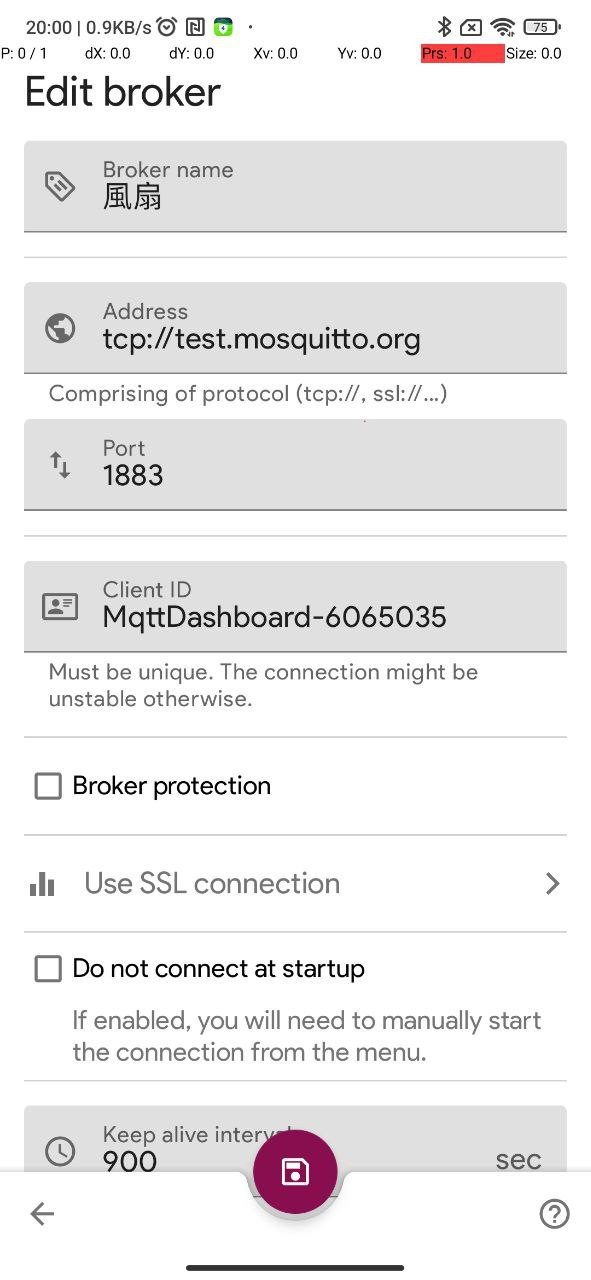
底部中間有一個磁碟片圖示,按下即可儲存設定
進入到 ”風扇“ 這個 Broker 裡再做設定動作,點選底部的 ”+“ 進入設定:
我們風扇在 MQTT 訂閱的主題是”Fan/Control",因此我們在 publish 中發送的主題也需要是同一個。
由於我們要產生四個按鈕:
電源:電源開關,送出 "power" 訊息
擺頭:擺頭開關,送出 “swing” 訊息
加: 風扇風速增加一檔,送出 “up” 訊息
減: 風扇風速降低一檔,送出 “down” 訊息

這樣在手機上操作,還真像是定製的應用軟體 !
我們可以用昨天在板子上訂閱 MQTT 的例子來試試,看看手機按下的按鈕發送訊息,板子能不能收到。若一切正常,接下來可以修改第27天所展示的變頻電風扇主控制程式。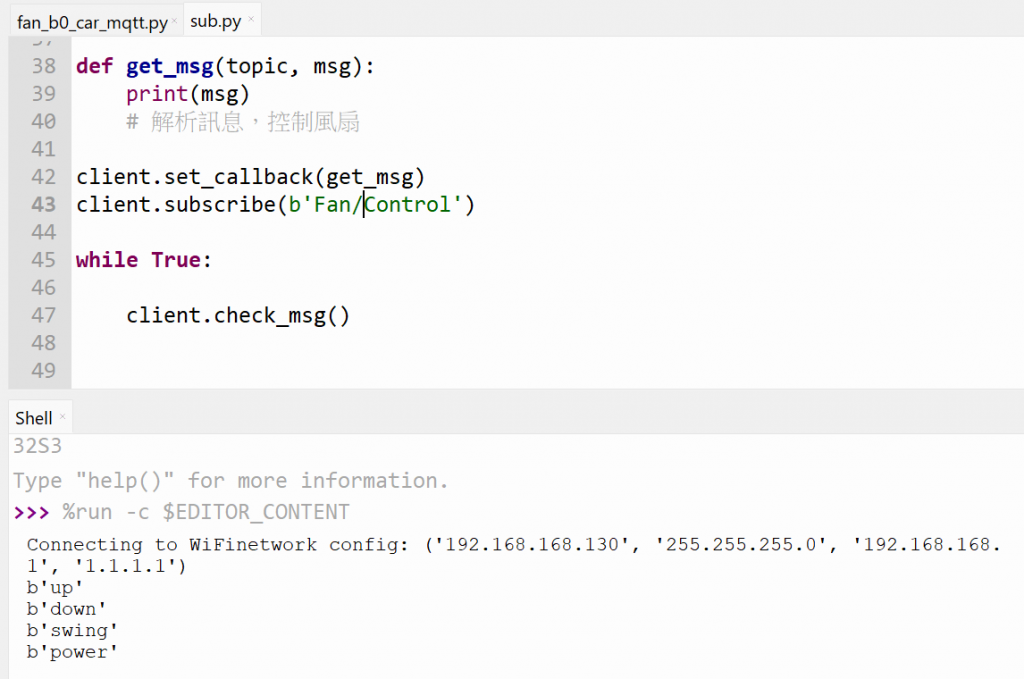
可以看出,驗證 OK,開發板可以正確收到手機發送出來的訊息
我們將這些訊息轉化成控制指令,修改之前的控制程式,整合之後的程式碼如下:
from machine import Timer, Pin, SoftI2C
import FourDigitDisplay as FDD
import time
from umqtt.robust import MQTTClient
import ubinascii
import machine
from micropython import const
from ir_rx.nec import NEC_8 # NEC remote, 8 bit addresses
IR = Pin(2, Pin.IN)
buzz = Pin(7, Pin.OUT, value=0)
speed_ctl = Pin(6, Pin.OUT)
swing = Pin(3, Pin.OUT, value=0)
# IR code
ADDR = const(0)
PWR_ON = const(0x43)
SPD_UP = const(0x47)
SPD_DN = const(0x45)
SWING = const(0x46)
TMR_UP = const(0x15)
TMR_DN = const(0x7)
i2c = SoftI2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=10000)
fdd = FDD.FourDigitDisplay(i2c)
#i2c.scan()
fdd.clear()
ir_code_old = 0
ir_code_new = 0
speed = 0 # Hz
fan_on = False
swing_on = False
t0 = Timer(0)
def toogle_speed(t):
speed_ctl.value(not speed_ctl.value())
def change_speed(speed):
global t0
global fdd
if (speed):
t0.init(freq=speed*2*50, mode=Timer.PERIODIC, callback=toogle_speed)
else:
t0.deinit()
fdd.showbit(int(speed),3)
def beep():
buzz.value(1)
time.sleep_ms(100)
buzz.value(0)
def ir_cb(data, addr, ctrl):
global ir_code_new
global ir_code_old
global ADDR
if data < 0: # NEC protocol sends repeat codes.
print('Repeat code.')
else:
print('Data {:02x} Addr {:04x}'.format(data, addr))
if (addr == ADDR):
ir_code_new = data
ir_code_old = 0
ir = NEC_8(IR, ir_cb)
client = MQTTClient(
#client_id="client_test_fan_sub",
client_id=ubinascii.hexlify(machine.unique_id()),
keepalive=60,
server="test.mosquitto.org",
ssl=False)
client.connect(False) # robust 模組,這裡填 False
def get_msg(topic, msg):
global ir_code_new
global ir_code_old
print("MQTT: ",msg)
# 解析訊息,控制風扇
# 以下借用 紅外線的控制碼來控制風扇,所以讓主流程都不需要更改!
m = msg.decode("utf-8")
if (m == 'power'):
ir_code_new = PWR_ON
ir_code_old = 0
elif (m == 'swing'):
ir_code_new = SWING
ir_code_old = 0
elif (m == 'up'):
ir_code_new = SPD_UP
ir_code_old = 0
elif (m == 'down'):
ir_code_new = SPD_DN
ir_code_old = 0
client.set_callback(get_msg)
client.subscribe(b'Fan/Control')
# power on beep()
beep()
beep()
beep()
beep()
while True:
time.sleep_ms(100)
client.check_msg()
if (ir_code_new == ir_code_old):
continue
print('Cheking...')
beep()
ir_code_old = ir_code_new
if (ir_code_new == PWR_ON):
if (fan_on == True):
speed = 0
fan_on = False
swing_on = False
swing.value(swing_on)
change_speed(speed)
fdd.clear()
beep()
time.sleep_ms(200)
beep()
print('Off')
else:
fan_on = True
speed = 1
change_speed(speed)
print('On')
continue
if (fan_on == True):
if (ir_code_new == SPD_UP): # increase speed
speed += 1
if (speed > 8): speed = 8
change_speed(speed)
elif (ir_code_new == SPD_DN): #decrease speed
speed -= 1
if (speed < 0): speed = 0
change_speed(speed)
elif (ir_code_new == SWING): #swing
swing_on = not swing_on
swing.value(swing_on)
print('Done...')
